Does applying LED strip technology to infrared (IR) lighting open up entirely new application scenarios and make it easier to access the home and personal user markets?
While traditional LED light strips are dominated by visible lighting, IR LED light strip uses special wavelength near-infrared (NIR) LED light sources that function in the invisible spectrum, offering new possibilities for security, biosensing, health monitoring and even intelligent interaction.
Similarly, UV (Ultraviolet) LED light strips also belong to special wavelength lighting, but their application logic is very different – IR and UV, which happen to be located at the two ends of the electromagnetic spectrum.
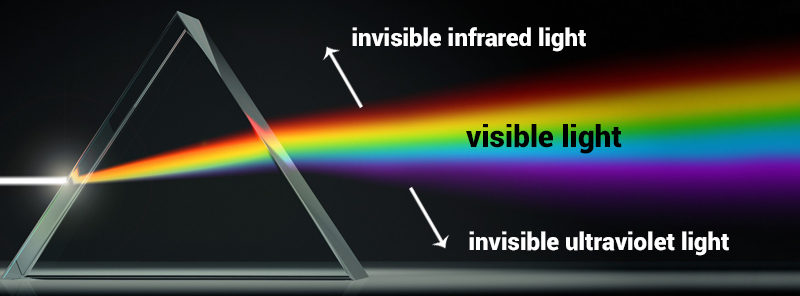
What Does Infrared Light Look Like?
In 1800, British astronomer William Herschel discovered the region just beyond the visible red light (with wavelengths longer than the red spectrum) registered higher temperatures, while measuring the temperature of the solar spectrum. These invisible “heat rays” revealed the existence of what we now know as infrared radiation for the first time in history.
The most amazing characteristic of LED infrared lights is that it is essentially an “invisible light”. Although infrared rays are invisible to our eyes, you have already experienced infrared light through your other senses:
- The warmth of the sun: about 53% of the energy in sunlight that hits the skin comes from infrared (especially far infrared).
- The gray and white world of night vision surveillance: house security cameras turn the picture into a high contrast black and white image at night when in 850nm/940nm infrared fill light mode.
- Plant health monitoring: agricultural multispectral cameras show the near infrared reflected by plants with false-color images (healthy leaves are bright red).
Interestingly infra red light itself has no color – at least not on the color palette of human vision. In optics, color is the brain’s interpretation of specific wavelengths of visible light, such as the 620 nm wavelength we call red light.
Cone cells in the human retina are unable to respond to light greater than 780 nm, and the spectrum of infrared light used for illumination is primarily between 780-1000 nm.
| Wavelength | Spectrum | Frequency | Photon Energy | Visibility | Penetration Depth | Heat Generation Efficiency |
| 780nm | Close to visible light | High | High | Slightly red | Surface layer | Low |
| 810nm | Near infrared light | Higher | Higher | Not visible | Epidermis + superficial dermis (texture), plant stem | Low |
| 850nm | Near infrared light | Medium | Medium | Red glow (red leakage, red spill) | Epidermis + superficial dermis (vein outline), canopy penetration | Low |
| 910nm | Near infrared light | Lower | Lower | Not visible | Full dermis + subcutaneous tissue (absorbed by adipose tissue), plant moisture reconnaissance | Medium |
| 940nm | Near infrared light | Low | Low | Not visible | Subcutaneous and deeper, fruit status detection | Medium |
| 970nm | Near infrared light | Minimum | Minimum | Not visible | Subcutaneous and deeper, precise moisture measurement | High |
Can Humans and Animals See Infrared LED Light?
Humans and most animals such as dogs, cats, deer, and coyotes cannot see infrared light because the wavelengths of infra-red light are beyond the range of our photoreceptor cells. Some snakes and some insects can perceive infrared light.
How to View and Detect Light on Infrared LED Strip?
Although human beings cannot directly perceive infrared LED lights, we can effectively view and detect the light emitted by infrared LED strips through specific devices and technologies such as infrared night vision, infrared thermal imagers, infrared detectors, infrared sensors, infrared filters, and smartphone cameras.
Tip: Please do the detection of infrared LED light strip in a dark environment. Visible light will interfere with the near-infrared signal.

Infrared Light vs Red Light
Although infrared and red light are spectrally adjacent, they are significantly different.
Red light is part of the visible spectrum and has a wavelength range of approximately 620 nanometers to 750 nanometers. It is the light that the human eye can perceive directly and appears in the familiar red color.
Infrared light lies outside the visible spectrum and has a wavelength range from 750 nanometers to 1 millimeter. Infrared light can be further classified into near-infrared light (750 nanometers to 3 microns), mid-infrared light (3 microns to 8 microns), and far-infrared light (8 microns to 1 millimeter). Infrared light is invisible to the human eye, but can be detected and imaged with specific equipment such as infrared cameras and thermal imagers.

Red light is often used for decorative lighting, special red light wavelengths such as 660 nm LED and 730 nm LED would be used for red light therapy and plant supplementation; infrared light is more specialized, and is often used in areas that require specific technical equipment such as security camera systems, healthcare, communications, remote sensing, and environmental monitoring.
Infrared Light Therapy vs Red Light Therapy:
As examples of non-invasive treatments, red light therapy (RLT) and infrared light therapy (ILT) primarily utilize specific wavelengths of light to stimulate cellular function. Aside from the visible and invisible differences, the main difference between RLT and ILT is the ability of the light wavelengths to penetrate.
Red light has a relatively shallow depth of penetration, typically reaching only the outer and middle layers of the skin, making it highly effective in treating surface skin problems such as acne and superficial wounds.
In contrast, infrared light has a much greater ability to penetrate deeper into muscles, joints and even bones. Therefore, infrared light therapy is more effective in treating deep tissue problems such as muscle pain, arthritis and neuralgia.
Derivation: Home Infrared Sauna with Red Light Therapy
The emergence of red light therapy sauna at home is a product of the combination of modern technology and traditional health care concepts. Often people choose to combine red light therapy with infrared light therapy for home sauna to achieve overall health improvement from the epidermis to the deep tissues – – repairing skin elasticity, dilating blood vessels, relieving muscle stiffness, and assisting in chronic pain management.
Traditional saunas raise the body temperature by heating the air to achieve detoxification and wellness, but the high temperature may aggravate the burden on the heart and lungs.
Infrared sauna uses infrared heaters to directly heat the human body, infrared light penetrates directly into the body and gently heats the core of the body to promote blood circulation and metabolism, which is more efficient and more comfortable (usually 40-60℃ can achieve the effect).

Is Infrared Light Harmful to Eyes and Skin?
Are red and infrared light rays absolutely safe for direct exposure to the human body, even though they are not visible? In fact, the potential effects of different wavelengths of light radiation on the eyes and skin vary dramatically – from short-term warmth and healing, to long-term or high-intensity exposure that can cause “invisible damage”.
Red light is generally considered safe, however, high intensity red light can penetrate the retina causing eye damage and thermal damage to the skin. Near-infrared light can cause damage to the retina and lens. Even when the eyes are closed, near-infrared light can still be a threat to the eyes: the eyelids only partially block near-infrared light. The lens acts as an “infrared vacuum cleaner” – absorbing up to 50% of the 900-1000 nm wavelengths.
Prolonged exposure to high-intensity NIR lights can also lead to cataracts, and collagen and elastin mechanisms can be disrupted, leading to skin aging. Although the direct link between NIR light and skin cancer has not yet been clarified by research, long-term exposure may indirectly affect skin cancer risk.
The use of red and near infrared light therapy may aggravate the reaction if people with photosensitive skin diseases or those who are using photosensitive medications, please consult your doctor for details.
Proper Use of LED Red and Infrared Light Products
Even when emitting red and near-infrared light waves directly, the light intensity and infrared radiation achieved by LED light strips are usually well below the hazardous values, but it is still necessary to avoid looking directly at red and infrared LED light sources for long periods of time, and to wear goggles if necessary.
Professional red/infrared light panels (e.g. beauty salons, therapeutic devices) have higher radiation intensity and should be used scientifically to avoid potential risks and at a safe distance.
Examples of hazardous scenarios:
- Prolonged daily exposure to red and infrared light
- Looking directly into a high-intensity infrared light
- Shining an infrared laser in your eyes
Remember: Red and infrared light are not like sunlight that makes you squint and dodge, so be careful with any LED product that can cause “invisible damage”.