
Near-infrared light (NIR, 700 – 2500 nm), as an “invisible light” in the electromagnetic spectrum, is widely used in fields such as medicine healthcare, plant production, industrial inspection, and communications due to its unique penetration capabilities and low thermal effects.
However, near-infrared LEDs of different wavelengths (such as 850 nm and 940 nm) exhibit significant differences in performance and application—from tissue penetration depth to material absorption rates, the NIR wavelength selection directly impacts the final outcome. This article breaks down key NIR light characteristics and guides you in selecting the optimal wavelength for your application.
What is Near Infrared Light & Its Applications
NIR near-infrared light is electromagnetic radiation that lies between visible light and mid-infrared light, with a wavelength range typically spanning 700 to 2,500 nanometers.

Depending on wavelength, it can be further categorized into:
Short-wave near-infrared (SW-NIR, 700 – 1400 nm)
Short-wave near-infrared (SW-NIR, also called NIR-A) is the wavelength band in the near-infrared spectrum closest to visible light, possessing unique physical and biological properties. A key advantage of this NIR band is its strong tissue penetration capability (up to several centimeters deep) combined with extremely low heat generation, making it an ideal choice for non-invasive therapy and bioimaging.
For example, the 730 nm far-red NIR light excels in skin phototherapy, effectively promoting collagen regeneration and improving skin condition. 850nm near infrared light LEDs serve critical roles in medical devices such as phototherapy units and pulse oximeters, as they can effectively penetrate the skin and detect hemoglobin concentration. In clinical treatment, 810 nm near-infrared LED light band is widely applied in neuro-regeneration and dental therapy due to its selective stimulation of deep tissues.
In industrial applications, 940nm near infrared led lighting dominates security surveillance and facial recognition systems, as this wavelength is difficult to detect in nighttime imaging while maintaining excellent signal-to-noise ratio.

Additionally, SW-NIR has important applications in plant growth regulation. The red edge band (680 – 750 nm) is the starting point of near IR-A, characterized by strong chlorophyll absorption and leaf reflection, closely related to vegetation photosynthetic capacity.

Long-wave near-infrared (LW-NIR, 1400 – 2500 nm)
Long-wave near-infrared (LW-NIR, also called NIR-B) has longer wavelengths and is more easily absorbed by water and organic molecules, playing an irreplaceable role in component analysis and industrial detection.
For instance, near IR-B wavelengths such as 1450 nm and 1940 nm are highly sensitive to water absorption, so they are often used in agricultural moisture detection (e.g., grains, tea) and pharmaceutical quality control. In the plastic recycling industry, LW-NIR (e.g., 1200 – 1700 nm) can accurately distinguish between different polymer types (such as PET and PVC), enabling efficient sorting.
In remote sensing, LW-NIR (particularly the 1500 – 2500 nm band) can precisely identify surface mineral composition and vegetation biochemical parameters through satellite-borne hyperspectral imaging, providing critical data support for environmental monitoring and resource exploration.

However, LW-NIR has limited penetration depth and requires higher-power light sources, which restricts its application in biomedicine. Nevertheless, LW-NIR light remains a viable tool in skin therapy.
The unique advantages of near-infrared lights include:
✅ Non-invasive – It can penetrate skin and tissue without causing harm.
✅ Low thermal effect – Compared to mid- and far-infrared light, NIR does not produce significant heat, making it more suitable for prolonged exposure.
✅ High signal-to-noise ratio – In spectral analysis, NIR is less susceptible to background interference, resulting in higher detection accuracy.
Understanding NIR LED Wavelengths
The core value of near infrared led light strips lies in their wavelength specificity—different wavelengths interact uniquely with materials, unlocking entirely different application scenarios.
By understanding the characteristics and applications of NIR infrared LED at different wavelengths, you can better select products suited to your needs and achieve optimal application results.
The commonly used near-infrared light wavelengths in LED applications primarily include 700nm, 710nm, 720nm, 730nm, 740nm, 750nm, 760nm, 770nm, 780nm, 790nm, 800nm, 808nm, 810nm, 820nm, 830nm, 840nm, 848nm, 850nm, 855nm, 858nm, 860nm, 870nm, 880nm, 900nm, 910nm, 920nm, 930nm, 935nm, 940nm, 944nm, 945nm, 950nm, 960nm, 970nm, 980nm, 1050nm, 1070nm, 1100nm, 1200nm, 1300nm, 1400nm, etc.
3 important NIR light wavelength nodes
To help you remember and quickly distinguish these near-infrared LED wavelengths, we have selected three important nanometer nodes. By remembering these NIR LED wavelength nodes, you can roughly distinguish the visibility of these infrared wavelengths and their approximate application directions.
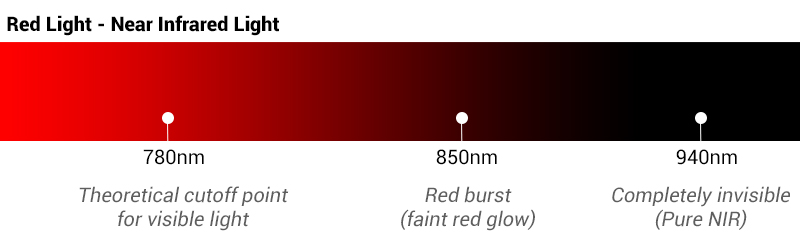
- 780nm: Widely regarded as the theoretical cutoff point for visible light. Near infrared light emitting diodes LEDs below 780nm emit a distinct red light spot that is clearly visible to the naked eye.
- 850nm: Although it falls within the invisible light spectrum, 850nm LEDs may exhibit a faint red glow due to spectral leakage (especially in dark environments).
- 940nm: Completely invisible, completely eliminating red glow issues, ideal for covert surveillance (such as facial recognition) and biomedical sensing (such as non-invasive detection). A smartphone camera or professional testing instrument is required to verify the operation of 940nm LEDs.
Choosing the Right NIR Wavelength
After learning about the characteristics and common wavelengths of near-infrared light, you may be faced with the following dilemma: “Should I use 850 nm or 940 nm for my project? Is 1050 nm worth the higher cost?” The choice of NIR region wavelength is not simply a matter of “the less visible the better” or “the deeper the penetration the better.” Instead, it requires comprehensive consideration of three dimensions: detection target, environmental interference, and cost-effectiveness.
NIR LED Wavelength Selection Guide
| Near-Infrared Wavelength LEDs | Visibility | Cost | Price/LED (USD) | Core Advantages | Typical Industries | Absorbing Substances |
| 700-750nm | Yes (red light) | Low | $0.10 – $0.50 | Plant growth, basic phototherapy | Agriculture, beauty | Chlorophyll D |
| 755nm | Yes (dim red) | Low | $1 – $5 | Alexandrite laser, pigment treatment | Dermatology (epidermal / dermal pigmentation) | Oxyhemoglobin |
| 780nm | Vis-NIR cutoff point | Medium | $2 – $10 | Diode laser applications | Periodontal treatment, Skin treatment | Hemoglobin (weak), Melanin |
| 808nm | No (weak red glow) | Medium | $5 – $30 | Semiconductor laser, photothermal therapy | Oncology, physiotherapy | Hemoglobin, etc. |
| 810nm | No (weak red glow) | Medium | $5 – $25 | Diode laser, nerve repair | Neurology, dentistry | Hemoglobin |
| 830nm | No (weak red glow) | Medium | $3 – $15 | Low-level laser therapy (LLLT) | Anti-inflammatory, pain relief, wound healing | Hemoglobin, Cytochrome C oxidase |
| 850nm | No (weak red glow) | Low | $0.50 – $3 | High-power LEDs, oximetry, brain imaging | Medical diagnostics, home care | Hemoglobin (deoxy-) |
| 855-900nm | No | Low | $1 – $8 | Industrial sensing, night vision | Security, automotive | Water (weak), tissue scattering |
| 910nm | No | High | $10 – $50 | Vascular therapy, deep tissue penetration | Medical, dermatology | Hemoglobin |
| 920-935nm | No | Medium | $8 – $40 | Fat reduction, lymphatic drainage | Aesthetics, wellness | Lipids, Water |
| 940nm | No | Low | $0.80 – $5 | Dental procedures, coagulation | Dentistry, surgery | Water, Hemoglobin |
| 945-960nm | No | High | $15 – $70 | Fat melting, skin tightening | Cosmetic surgery | Fat, Water |
| 970nm | No | Very High | $20 – $100 | Precision ablation, surgical applications | Medical lasers | Water, Hemoglobin |
| 980nm | No | High | $10 – $60 | Yb fiber laser, varicose vein treatment | Vascular surgery | Hemoglobin, Water (strong absorption) |
| 1064nm | No | Very High | $50 – $200+ | Nd:YAG laser (deep vascular, lithotripsy, ophthalmology) | Medical, industrial | Water, Melanin |
| 1070nm | No | Very High | $50 – $300+ | Fiber laser (fat decomposition, fascia release) | Aesthetic medicine | Water, Fat |
| 1200nm | No | Very High | $100 – $500+ | Tissue ablation, optical imaging | Research, medical diagnostics | Water |
| 1320nm | No | Very High | $200 – $1000+ | Nd:YAG laser (non-ablative skin tightening, EVLT) | Dermatology, vascular surgery | Water |
| 1400nm | No | Very High | $150 – $800+ | Skin resurfacing, industrial cutting | Aesthetics, manufacturing | Water (strong absorption) |
Multi-Wavelength Collaborative Solutions
In practical applications, single-wavelength near-infrared light often fails to meet the demands of complex scenarios. By scientifically combining near-infrared light sources of different wavelengths like red and blue, synergistic effects can be achieved, significantly enhancing treatment efficacy and application value.
660nm + 850nm Combination
In wound healing therapy, 660nm red light promotes epidermal cell proliferation, while 850nm near-infrared light penetrates subcutaneous tissue to improve microcirculation. The synergistic effect of both can accelerate the wound healing process by over 30%.
In sports rehabilitation, this 660nm and 850nm red and NIR combination can simultaneously alleviate superficial muscle pain and deep tissue inflammation.
450nm + 660nm + 810nm Three-Wavelength Combination
In oral treatment, 450nm blue light sterilizes, 660nm red light promotes gum repair, and 810nm near-infrared light stimulates alveolar bone regeneration.
In neuropathic pain treatment, the synergistic effect of the three wavelengths provides comprehensive treatment from the epidermis to nerve endings.
730nm + 850nm Combination
In skin anti-aging treatment, the 730nm and 850nm near infrared combination achieves a three-dimensional effect of “superficial repair + deep stimulation.”
In agriculture, it promotes the entire growth cycle of plants, from photosynthesis to nutrient absorption.
810nm + 980nm Combination
In neurological rehabilitation, the 810nm and 980nm simultaneously achieve nerve stimulation and microcirculation improvement.
In medical aesthetics, it can simultaneously perform skin tightening and vascular treatment.
This multi-wavelength synergistic approach not only enhances treatment precision but also significantly expands the application boundaries of near-infrared technology, bringing revolutionary solutions to the medical, agricultural, and industrial fields.